


 |
United Earth/Oceans Organization (UEO) |
| Circa: 2017 - 2022 | |
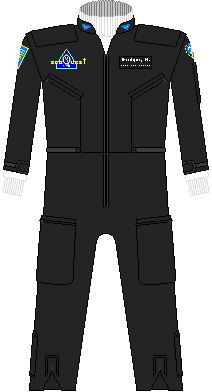
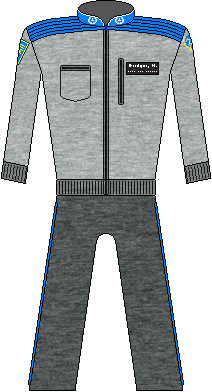
Partially refitted as a deep submergence research vessel, the seaQuest now included a large science contingent (122 science/88military). It was hoped that the new peace would hold and eventually the vessel could have all its armaments removed to allow the space to be used for additional scientific research. In the meantime however, a less-militaristic uniform was needed and the UEO selected a simple black jumpsuit with colored undershirts for their uniforms. Meanwhile the science contingent adopted a nearly identical blue jumpsuit for utility purposes. | |
 |
United Earth/Oceans Organization (UEO) |
| Circa: 2021 - 2035 | |
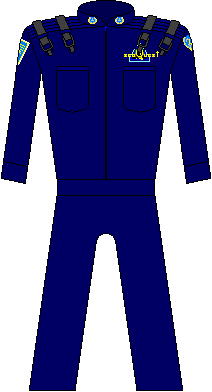
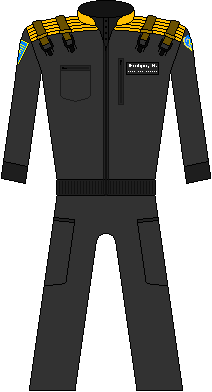
Following Captain Bridger's decision to use the seaQuest's nuclear capacity to seal a massive lava well off the Australian coast in early 2020; the political infighting and economic greed of humanity came roaring back to the forefront. The three years it took to build a second seaQuest left the UEO bankrupt of influence around the globe; and during the Economic Summit of 2026, the UEO had no choice but to lift the ban on colonial deregulation, putting a quarter million square kilometers of prime ocean real estate back on the market. With a new seaQuest, came a new assumption of power, and the UEO redesigned its uniforms to go with the grittier, more hostile times. Since their sub crews were tasked with protecting both the people living and working in the oceans as well as the natural life, it was decided to merge the black and blue into a dark blue jumpsuit and add features for increased combat utility. | |
 |
United Earth/Oceans Organization (UEO) |
| Circa: 2033 - 2044 | |
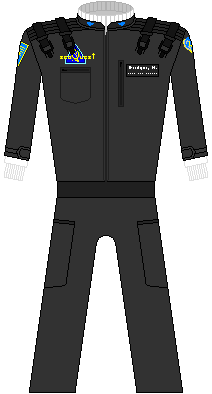
With the increasing frequency of hostile interactions between the UEO, Macronesia, and the Chaodai Empire; it became painfully obvious that war in the Pacific was a question of when, not if. The increasing calls for religious unity on the Arabian Peninsula combined with the continued retreat of Indian and Pakistani socio-economic engagement with the west; left the unmistakable conclusion that a military buildup by the western powers was no longer avoidable. As a result, UEO Command ordered seaQuest back to the New Cape Quest drydock for refit back to a fulltime warship. A small science contingent (173 military & 21 science) and facilities remained aboard as a token promise to the future (but also because the science crew had shown their worth in military situations on multiple occassions). | |
 |
United Nations Armed Forces |
| Circa: 2044 - 2059 | |
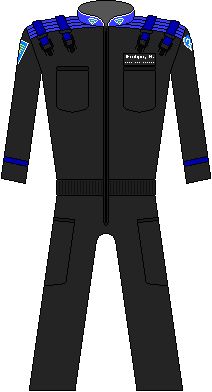
With the formation of the Eastern Coalition, the Western Countries realized they needed to take drastic action to survive. Talks were begun and soon it was decided to merge the United Nations and the United Earth/Oceans Organization into a single political entity. As the only remaining independant nations, the Afrikaan and Amazonian Confederations signed into the merger as well. The basic design of the uniform was taken from the UEO service uniforms, while the specific shade of blue was selected from the United Nations flag. This uniform would carry the United Nations (of Earth, UNoE) through the conventional conflict as well as the horror of the nuclear holocaust which eliminated over a third of the remaining population of humanity. | |
 |
United Nations Armed Services |
| Circa: 2055 - 2063 | |
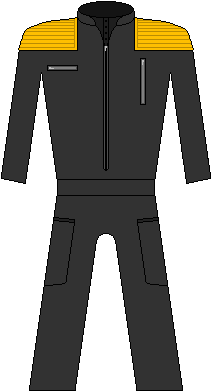
Following the cessation of hostilities and the 24-Dec-2054 surrender of the Secretariat of the Eastern Coalition; the United Nations of Earth (UNoE) looked to reduce their image of combat intentions and redesigned the uniforms used by their international law enforcement and peacekeeper units. Retaining the trademark light blue of the UNoE, the military black jumpsuits were redesigned using a two-tone heather-grey base color; chosen to represent the ashes of the those killed during the war as well as the metaphorical ashes of humanity's past. They also abandoned the modular shoulder buckles as well. | |
 |
United Earth Services |
| Circa: 2063 - 2101 | |
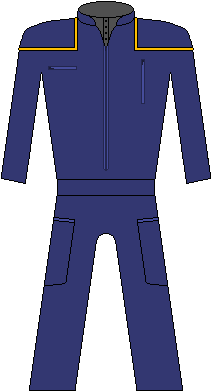
Following Zefram Cochrane's warp flight aboard the Phoenix, mankind began recognizing the inevitability of a post-scarcity economy. The establishment of true international cooperation began with the United Earth Service; an agency that assumed the responsibility of maintaining public utilities around the planet. With the continued need for rebuilding of so much of Earth's infrastructure, the need for additional material resources exceeded everything terrestrial sources could provide and as a result, UES began working on plans to start mining the moon and then the asteroid belt. | |
 |
United Earth Space-Probe Agency |
| Circa: 2095 - 2130 | |
Space... the unlimited frontier. Metals found in the lunar regolith and asteroidal crusts provided a massive influx of materials needed to turn Earth from a resource-scarce backwater into a powerhouse of innovation and advancement. To provide for the ample extraction and refining of thes resources, the United Earth Parliment founded the UE Space Probe Agency with the basic goal of providing the most efficient harvesting and refining of materials to help rebuild Earth It was the UESPA which led to the discovery of dilithium as well as advanced metal-ceramic alloys that would ultimately lead to the alloys needed for modern warp coils and other advanced technologies. As UESPA advanced science, science advanced technology, and technology advanced space-exploration. | |
 |
United Earth Starfleet |
| Circa: 2129 - 2161 | |
As Earth sciences began discovering and developing more advanced space technology, UESPA could no longer provide the best service to both materials harvesting as well as exploration of both additional minable metals and ores as well as simply discovering new places to look. With UESPA stretched to the limit, the United Earth Parliment chose to create a new agency who's sole function was to expand humanity's ability to travel to the stars. And with the stroke of a pen, Starfleet was born and the former US naval construction docks in San Diego; the Jiangnan Shipyard in Shanghai; and were assigned as the new places of construction for humanity's burgeoning need for spacecraft. | |
